ВУЗ: Не указан
Категория: Не указан
Дисциплина: Не указана
Добавлен: 18.10.2024
Просмотров: 246
Скачиваний: 1
Unit
Before you read
Discuss these questions with your partner.
-* What is money?
-» Can anything be used as money?
Could stones and leaves be used instead ol coins and notes?
0 A Vocabulary
Choose the correct word or phrase.
One reason why people buy gold is because it
holds its value / is taken (or granted.
When we buy things, we money
for goods.
Diamonds are valuable because they are so
intrinsic / rare.
The dollar is the of the USA.
When people goods, they
simply exchange one good for another.
Banks will only lend to people who can to pay back the loan.
Some shops won't accept credit cards. They will only take
When something
people don't think it has great value.
Coins and notes are used to value.
Metals have value because they
can be used to make things.
If money can easily bo moved around and used we say it has
Centuries ago people paid using
. such as gold and silver.
.like
banknotes and coins, has no intrinsic value. It only represents value.

IF Reading 1
Money
The cash vve use every day is something we take for granted, hut for thousands of years people trailed without it. Ilefore money w;is invented, people used a system called hurt к rina Bartering is simply swapping one good for another. Imagine that you have milk, for example, and you want eggs. You simply l'ind someone who has eii£s and wants milk - ami you swap! However, you can set that this isn't a very convenient way to trade.
first of all. you can't be sure that anyone will want what you've got to offer. Yon have to hope that you'll be lucky and find someone who has what you want and that he or she wants what you've got The second problem with bartering is that many goods don't hold their value For example, you can't keep your milk for a few months and then barter it. Nobody will want it!
и
о
67
With commodity money, the thing used Юг buying goods has inherent value. For example, gold has inherent value because it is rare, beautiful and useful. Salt has inherent value Ivcause it makes food tasty. If you could buy things with a bag of salt, it meant you could keep a store of salt ami buy things anytime you needed them. In other words, commodity money can store value
I'sing commodity пюпеу was much more convenient than ordinary bartering, but it still had drawbacks < >nc of these drawbacks is that commodity пюпеу often lacks litfuulity Liquidity refers t.i how easily money can circulate There is obviously a limit to how much salt you can carry around1 t here's another problem with commodity money not everyone may agree on the value of
^ В Comprehension
Complete the table with information from the text.
1 lie commodity which is used as money. It you live by the sea. salt may not b@ SO valuable to you. Money needs to be а ц<мк1 unit о/шччшш. In other words, everyone should know and agree on the value of a unit. This way. money can be used to measure the value of other things.
The solution is to create a kind of money that does not have any real intrinsic value, but that represents value. This is calledJuit money. The coins and notes that wi use today are an example of fiat money. Notes don't have any inherent value
they are just paper. However, everyone agrees that they arc worth something. More importantly, their value is guaranteed by the government This is the reason why pounds and dollars and the world's other currencies have value.
|
|
Examples |
Advantages |
Disadvantages |
|
Bartering |
swapping eggs for milk |
simple to understand |
goods don't |
|
Commodity Money |
|
allows you to store |
not agrees on its value lack of liquidity means money can't |
|
Fiat Money |
|
value is (10) by the government |
|
Before you listen
Discuss the following with your partner.
You're
going to listen to someone talking about the history of mor.oy.
Before you listen, read through the statements below. Do you think
they are true or false?
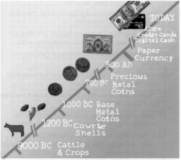
used
about 3.000 years ago.
tD/fD
2
Shells were used
ляa kind of
fiat
money.
tD/fD
3The first metal coins appeared
in
Greece.
tD/fD
4The first coins were round.
tD/fD
5Paper money first appeared
in
China.
tD/fD
6The idea of paper money travelled
quickly
to Europe.
tD/fD1 The earliest kind of money was
68 M » r m * * Gui4| t f- f ' лллп1м и a» t 13
В с Listening Ц)))
Before you read
Discuss the following with your partner.
-* What do banks do? Work with a partner to make a list of all the services that banks provide. Then compare your list with others in the class.
0 D Vocabulary
Complete each sentence with a word or phrase from the box.
accessible ATM 'compensate deposit make a living reliable I security sensible • transfer withdrawal
As against possible burglaries, they
installed alarms.
Some people aren't very with their
money and they waste it on useless things.
If you are injured at work, you may get money to for losing your salary.
If something is you can trust it to
work properly.
things are easy to reach or to get.
When you things you move them
from one place to another.
7 An is a machine that gives
customers money when the bank is closed.
Most people have to work m order to
• When you make a you put money
into your account.
When you make a you take money
out of your account.


Banks
If you work, you've probably got a bank account. You eoukl keep tlu- money you earn each month in a Ikix under your bed. but it wouldn't be very sensible. < >ne reason is that it's not very salt It your house yets burgled, you'll lose everything you've saved Another reason is that your money will lose value.
As prices rise, the money in a l*>\ under your bed will be able to buy fewer and fewer things. Monev in a bank savings account, however, will earn interest. The interest will help compensate lot the effect of inflation. Hut banks are more than just safe places for your money What other services do they offerV
The other main service is lending money Individuals and businesses often need to I юг row money, and they need a lender that they can trust This is exactly what banks are - reliable lenders, hi fact, most of the monev that people deposit in their bank accounts is immediately lent out to someone else.
M
, t • ' ft t i 69
Bui how Jo banks make a livingV Basically. they make a living by charging interest on loans. < )t course, when you make a deposit into a bank savings account, the bank pays yon interest on that money However, the rate they pay savers is less than the rate they charge borrowers The extra money they make by charging interest on loans is where banks earn most of their money
l or banks, interest is also a kind of security. Sometimes people do not pay back money they borrow This is called liefaultim• on ц When
someone defaults on a loan, the bank uses money earned from interest to cover the loss.
All of this means that most of the money people have saved in the bank is not there at all! Л small amount of the total savings is kept by tin bank so that customers ean make withdrawals. The rest, however, is made available for loans. The amount that is kept is called the rc.svrcc. The reserve must lie a certain percentage of all the savings received from customers - for example JO per cent. This figure is set by the central bank, and this is one of the ways that governments can control the amount of money circulating in the economy.
В E Comprehension
Now read the text again and answer these questions in your own words in the space provided below.
W1i.it two reasons are given for saving your money in a bank account?
Why do people prefer to borrow money from banks?
Do banks do anything else for their customers other than store and lend money?
How do banks earn money?
Who decides how much money the bank keeps in reserve?
Before you listen
Discuss these questions with your partner.
If a bank note is not real, we call it a takeorcounterfeitnote.
-» How do you know if a banknote is real or not?
What can banks do to make people trust their notes and coins?
F Listening Ц)))
Look at these notes about whether a ten-pound note is genuine or not and see if you can guess what goes in the gaps.
Paper is very (1)
The words (2) are raised from the
paper.
There should be a strip of f3)m the
middle of the note
There is a watermark of the (4)
There is a hologram which shows a picture of
Britannia, who was a (5) and the
(6)
With a magnifying glass you can see the word f7) written in tiny microlettering.
If you put the note under fluorescent light, a bright (8).. number ten will appear.

70
M. an i«
Eroifi* т i if- t о
G Speaking
Discuss these questions with your partner.
Can you imagine life without money?
What are the dangers ol using a credit card to pay with instead of money?
What do you know about digital money?
Task
Give a two-minute presentation on the history of money. First, read through text 1 again and make notes below on the following.
bartering commodity money fiat money

Pronunciation guide
Liquidity ilwubti Copper knjvxri Accessible дк sesobl Deposit1ii i iliptvit Withdrawal wiA'drr>s>l Borrower lint.>>oir) Default <li i.i:i! Bartering f-xrurtq Fiat 11..W
Write a promotional leaflet for a bank.The aim of the leaflet is to attract new customers and to inform existing customers about the services the bank offers.
Use an informal, friendly style like you see in advertisements. Organise the leaflet using the plan ah.o4mh.ero.
Promotional leaflet
PARAGRAPH 1
Give a brief history of the bank and say how big it is today (to give confidence to customers).
PARAGRAPH 2
Explain what your main services are. and what advantages you ofte.rcompared to other bankR (for example, interest rates).
PARAGRAPH 3
Say what other services you offer and how they can be useful to your customers: for example, special savings schemes for certain people (students / pension schemes for workers) and Internet banking.
PARAGRAPH 4

/
Write 200-250 words
A
4
A
Unit
Before you read
Discuss these questions with your partner.
72
Hk ^
illm Gi'df to Fro46f"<<t Unit 14
ff A Vocabulary
Choose the correct answer А, В or С from the list opposite.
The department of the government
looks after roads, railways and airports.
l'hc government hopes its will help
reduce unemployment.
The parts that something is made of are sometimes called
4 employment is when everyone who
can work has a job.
The money that you have after you've paid taxes is called your income.
The part of a person's salary that is not taxed is called their personal
The government plans many new
projects, such as building new hospitals and schools.
Another word for extra goods that are not needed is
When the economy is working at full
it is using all its resources
for production.
A is a large, fast road which
connects cities.
A is a plan for achieving something.
In a tax syslem, people who earn
more pay more tax than people who earn less.
|
\ transport |
education |
defence |
|
' components |
allowance |
policy |
|
' income |
H components |
capacity |
|
■ absolute |
complete |
С full |
|
■ full |
disposable |
spending |
|
allowance |
surplus |
: capacity |
|
V personal |
public |
disposable |
|
i. surplus |
shortage |
allowance |
|
\ employment |
income |
capacity |
|
path |
motorway |
railway |
|
'> component |
1project |
1scheme |
|
'• surplus |
progressive |
public |