ВУЗ: Не указан
Категория: Не указан
Дисциплина: Не указана
Добавлен: 18.10.2024
Просмотров: 233
Скачиваний: 1
ways of measuring poverty
striking facts about poverty in the world today
where pover ty exists
causes of poverty
how poverty affects people's lives
the poverty trap
! H Writing
Write a report describing the charts on pages 56 and 57.
First, read text 1 again. Then look carefully at figure 1 and figure 2. Use the outline plan to help you. Remember to include the following language:
The chart shows ...
It is clear from the figures that...
The majority of the population ...
A very small percentage of the population ...
about ' approximately almost
a quarter half / a third
In comparison ...
In contrast...
is owned by ...
earn...
Report
PARAGRAPH 1
Introduction.Say generally what the charts are about ■ use the titles to help you.
Begin like this:These charts show how wealth and income are distributed in the UK. Figure 1 shows ...
PARAGRAPH 2
Describe figure 1 in more detail. Say how
much of the wealth the top one per cent own. Compare this with the bottom 50 per cent.
Begin like this:Tigure 1 shows how unfairly wealth in the UK is shared out You can clearly see from the chart that...
PARAGRAPH 3
Describe figure 2 in more detail.Describe the perfect distributionshown by the blue line. Give examples from the chart. Describe the real distribution shown by the red line. Give examples from the chart. Say how much of the total income the lowest 40 per cent earn. Say how much of the total income the top 30 per cent of the population earn.
Begin like this:Figure 2 compares perfect distribution of income with real distribution m the UK. The blue line shows what happens if income is evenly distributed ...
PARAGRAPH 4
Conclusion.Explain briefly what the figures show about the UK economy.
Notes:
Pronunciation
guide
Inequality
'mikwnbti Modernised
'iiHKbnai/d Precious
piof.is Jewel
'<: ;u:ol Lorenz
curve (iJ.w кчл Poverty ртлн Associate'Л i о<л>|юи
Corruption
kor\pin Drought
dtaul Flood fl.ul
Schooling
vkuilnj
60 M j tm л• s.3и • 4 t; f ■' л г ;. m i U •> • t i'
devastating collapse fiscal policy
domestic
steady growth
monetary policy
recession
mechanism disposable income
interest
circulate
depression predictable
Before
you read
Discuss
these questions with your partner.
->
Micromeans small and
macromeans large.
What do you think
macroeconomicsis?
-*
How is it different from
microeconomics?
A
Vocabulary
Match
the words and phrases with the definitions.
something that happens
a method or tool for do;ng something
control of spending through taxation
money you have to spend after paying tax
L a serious slowing down of the economy
at a slow, unchanging rate
move around
control of the cost of borrowing and movement of money in economy
the members of the population able to work
something you know will happen
complete destruction
the cost of borrowing money
not foreign
a very bad period for the economy

Macroeconomics
In the 1930s one «>1 tlu worlds strongest economies suffered a devastating collapse. It was the American economy, and the disaster was the < «real Depression. The effect*, of the Great Depression were felt all around the world, and it brought about a change in eeonomie thinking Economists Ьсцап to realise that looking at the behaviour oi individual consumers and suppliers in the economy was not enough. Keoiiomists ami governments had t>> understand how tlu wliok economy worked. In other words, they had to have in understanding of macroeconomics
Microeconomics looks a I how the details of tin. economy work. Macroeconomics takes a few steps back and looks at the whole pieturi While microeconomics looks at supply and demand !<т a single product or industry, macroeconomics follows supply and demand patterns for the whole economy. Whereas microeconomics is about economic ev cuts <il himu .macroeconomics looks at how the domestic economy interacts with the economies of other countries
However, macroeconomics isn't only alxnil knowing what s happening in the economy. After the shock of the Great Depression, governments realised that an economy needs Ю be managed Most governments aim to have steady economic growth, to control inflation and to avoid recessions .histmanaging an individual businessisa hard enough task. How do you manage a whole economy? Governments have certaini>niIlliniumswhich help them to do this.

Tlit first ■>! tlu st mechanisms is jiscul j»>licy Fiscal policy refers to the tax system and to government spending. Ну increasing or decreasing the amount of lax people inusi pay. tin government can affect how much money jieoplc have available to spend {ttixjxisable inconu ). This, in turn, has an effect 011 demand in the market. By increasing or decreasing their own spending, governments can have .1 huge effect 011 tlu growth of the economy
The second mechanism is monetary }x>!icy.With its monetary {>o|iey. a government sets interest rates and also controls the amount of money that circulates in the economy. The interest rate the government sets inlliienees the rate that commercial banks set when tlu > lend money to customers Interest rates have a big impact 011 the economy For example, they can affect people s decisions about saving or spending money
The third mechanism is administratis aj>pr<»ich This is a range of tilings that governments do to increase tlu supply of goodsand services to the economy but without increasing prices Therein 1 numl>er of ways governments try to do this. For example, improvements in education and training can make the workforce more productive Investment in technology can make industry more efficient. < iovernraents can also change employment anil business laws to make tilt- market more competitive.
til
Hii.iIIh
6ui4> to Cr««n»>c> U• 11 11
Now read the text again and answer the questions.
Which countries were affected by the Great Depression? only America just America and Europe the whole world Which of the following is interested in foreign economies? microeconomics macroeconomics both micro and macro economics The three different mechanisms which governments use are ...
all concerned with how much money people have to spend.
aimed at improving education and training, all different ways of managing an economy. Which mechanisms involve changing interest rates? fiscal policy monetary policy administrative approach Which mechanisms might involve creating job training schemes for school leavers? fiscal policy I monetary policy administrative approach What do governments want to achieve with their macroeconomic policies?
to predict what will happen in the economy to create steady economic growth to combine different paths for economic growth
Before you listen
Discuss the following with your partner.
You're going to hear about the Great Depression the worst economic recession in recorded history. Before you listen, see if you can put these events in the order thai they happened.
-» the economy began to recover -* companies produced more goods for funire demand World War 2 began
people started selling their stocks and shares -» the stock market crashed -» people lost jobs and farmers left their farms people borrowed money to invest in slocks and shares demand began to fall
9 С Listening 4)))
Now listen and check your answers.
Before you read
Discuss the following with your partner.
In some ways, running a large economy is like running a small business. What do you think are the similarities and what are the differences?
ф D Vocabulary
Complete each sentence with a word or phrase from the box.
aggregate availability behave exports long run predict required short run trend
The price of a flight often depends on the of seats.
Tecluiology is making it easier and easier to changes in the weather.
When talking about the we mean
the total.
Some people very differently
when they go abroad.
The means in the next few weeks
or months.
The means in the coming years
or decades.
China's include all kinds of
manufactured goods.
Л lot of raw materials for
manufacturing arc imported.
Prices are still following a
to increase.
I^f Ro^Hinn 9
Aggregate demand and aggregate supply
When a company makes plans for how much to produce and what prices to set. it needs information. The company needs to predict the level of supply that will he required to meet demand. It needs to set prices that will keep the business running. In the same way. governments need this information for the whole economy The total level of demand for all products and services is called the <t!if>rebate denumd. The total supply- is called the иццгецate supply.
The demand for products and services is how much is wanted. For a company, the demand comes from customers, For a whole economy, things arc a little more complicated. Demand in the whole economy comes from the following.
from consumers, because they buy products and services (consumption)
from companies, because they invest money to build factories and buy- machines (investment 1
from the government, because they spend money on services and projects (government spending I
from exports, because these are sales to customers in other countries (export)
Real
National Income
Prkes
Figure
2:
Aggregate
Supply
I
O'H) run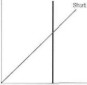
Figure
1: Aggregate Demand
A
Prkes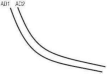
M u m j • G ■ <1 ♦ г ' ( . • -r. '. U r . ■ tj 63
Although aggregate demand is made up ol many tilings, it l/t hiiii s in the same way as demand tor a single produet For example, demand rises when incomes rise. The same applies to aggregate demand Similarly, demand falls as prices rise. The same is true for aggregate demand. You can see this relationship shown in tigure 1 on page o.V I'he vertical axis shows prices The horizontal axis shows real national income Real national income is the value of all the serv ices and products produced b> the whole economy. It's calculated in the same way as aggregate demand (consumption, investment, government spending and exports). You can see from the curve that national income (and therefore aggregate demand) increases as prices tall
Changes in any of the four things which make up aggregate demand will cause a shift in demand For example, if the government decides to spend a huge amount of money on building new hospitals and schools, this will have an effect on the whole economy. Aggregate demand will increase at all price levels. This is shown in aggregate demand curve 2 I Al>2) in tigure 1
l he supply curve for an individual produet or service is very simple As the company increases its supply to the market, it increases the price. But what about aggregate supply for the whole economy'' This is more complex. In the short run. aggregate supply follows the same trend as tlu supply for a single product. Supply rises as prices rise However, the long run is different In the long run. supply is not affected by price In the Jong run. production is limited by the factors of production In other words, what a country can supply de|4iids on the numlier of factories it has. the number of people working and the availability • >1 raw materials This is why the long run supply curve in figure 2 on page »>A is a straight liiu .
64
Магш111ая Gtiida to Есочеомс» Unit >2
BP E Comprehension
Now read the text again and match each paragraph with the correct heading.
PARAGRAPH 1
PARAGRAPH 2
PARAGRAPH 3
PARAGRAPH 4
PARAGRAPH 5
What aggregate demand includes
Two types of aggregate supply curve
The relationship between aggregate demand and price
Wiry are aggregate supply and demand important to governments?
What causes aggregate demand to shift?
Before you listen
Discuss the following with your partner.
The gross domestic product ( GDP) is a way of measuring the income of a whole nation.
-» How do you think GDP is calculated?
-» Why do you think some countries have a larger GDP than others?
Which countries in the world do you think have a large GDP?
Which ones have a small GDP?
0 F Listening *)))
Now listen and complete the summary.
The gross domestic product is the total value
of all the (1) supplied by a
country during a whole (2)
. It is often called the (3)
It is a way for the government to measure
the economic (4) of the
country. The GDP per capita is the GDP
divided by the number of (5)
It is a useful measure of a nation's
(6) In 2005. Luxembourg had
a per capita GDP of $ (2) In
the same year, the figure for Burundi was only $ (8)
ff G Speaking
Discuss these questions with your partner.
Why is it important for a coimtry to have steady economic growth?
The GDP of a country is sometimes used to measure standard of living. Do you think this is a good measure for standard of living? Why / Why not?
Task
Work in groups of three or four.The diagram below shows the aggregate demand and aggregate supply curves for a country.Talk to each other about how the curves could change for each of these situations.
the government decides to spend billions of pounds on road building
there is a large increase in the price of petrol
the government increases income tax rates by five per cent
wages increase a lot
Figure
1: Aggregate Demand and
Supply
Real
Hatwnal Oitput
Notes:
Prices
Imagine you're a farm worker in America in the 1930s.You've just lost your job because of the Great Depression. Write a letter to your cousin in Russia.
Look back at the unit and make notes before you start.
Letter from history
Dear [your cousin's name],
PARAGRAPH 1
Tell your cousin the bad news about losing your job and what difficulties you're facing.
Useful words and phrases:made redundant, struggle to got by, landlord demanding rent, bills to pay, go into debt
PARAGRAPH 2
Explain the situation in America: how the stock market crash happened, the Depression. Head the notes from С Listening on page 62.
Useful words and phrases:stock market, crash, fall in demand for produce, businesses closing down
PARAGRAPH 3
Explain what life is like in America now, especially for farmers and farm workers.
Useful words and phrases:high unemployment, families struggling to get by. people depressed, people leaving their homes for the city
PARAGRAPH 4
Say what you plan to do to find work.
Here are some ideas:move to the city to find work, join the army, try to sell something valuable you own and buy a ticket to Europe.
Sign off
Write 100-150 words
Pronunciation guide
Devastating 'dev.Weitnj Fiscal Tiskl
Mechanism 'mek.im/nm Monetary тлпнп Recession пм*|п Availability .iveibbtloii Axis ';ek<is
Match words from box A to words in box В to make expressions we use in economics.You can use words in box В more than once.
A
в?
В The words in bold in this newspaper story have been wrongly
printed. Put the letters in the correct order to make the right
word.
66
N1
a idftoEccioiT'rtRe.b 'Vcibji-t •
e t * rt>
demand gap goods income policy poverty scheme trap
Now match the expressions to their meanings.
services that the government provides because no one else will
services and goods that the government provides because they are good for us
not having enough money to survive
to be much poorer than other people in the same country
the government's decisions about taxation and spending
the government's decisions about interest rates and money in the economy
the money you can spend after you have paid tax
a situation in which it is impossible to escape from being poor
all the services and goods that are bought in the economy
a way to save money for old age
Revision
Vocabulary Units 9 to 12
Economic hard times set to continue
The government released more gloomy economic figures today. Unemployment lias risen again this mor.th. and now ten per cent of the (1) krowforec are without a job. At the same time, the Bank of England has said that (2) vinnetmestby companies lias decreased dramatically. 'Businesses simply don't want to be involved in (3) srki-agtkniwhen the economy is like this.' commented John Cash, a senior director with the bank.
But the people worst affected are the unemployed and their families. Many are now spending their life (4) gisvansin order to survive. Government Minister. Alison Wellby said yesterday that. 'The(5) frelwaeof ordinary people is our most important concern'. To prove this, the government has promised to increase spending on (6) frantres payments such as unemployment (2) fitsbeen. However, this could be a sign that the (8) cresseion will probably continue into next year. It seems that even in the (9) glon nurthings are not looking good.
S Find ten words in the square connected with buying and selling.
|
d |
w |
h |
о |
l |
e |
s |
a |
1 |
e |
r |
с |
b |
s |
|
к |
i |
d |
g |
с |
e |
X |
я |
t |
r |
e |
о |
q |
h |
|
v |
к |
s |
w |
r |
b |
e |
w |
r |
b |
) |
n |
n |
a |
|
u |
v |
w |
с |
b |
i |
d |
g |
с |
e |
d |
s |
к |
r |
|
d |
r |
b |
3 |
r |
g |
7. |
m |
о |
с |
t |
u |
V |
e |
|
s |
t |
t |
u |
к |
i |
t |
w |
г |
b |
i |
m |
u |
s |
|
о |
л |
X |
a |
V |
ri |
m |
a |
1 |
к |
u |
P |
d |
e |
|
e |
u |
z |
z |
u |
j |
h |
i |
7. |
u |
j |
t |
s |
b |
|
1 |
7. |
u |
j |
h |
e |
z |
u |
n |
b |
1 |
i |
о |
a |
|
Я |
С |
e |
X |
* |
i |
e |
'.V |
b |
a |
к |
0 |
e |
r |
|
i |
e |
t |
a |
i |
1 |
e |
r |
s |
V |
t |
n |
Р |
g |
|
t |
r |
e |
w |
t |
r |
e |
w |
b |
1 |
d |
l |
i |
a |
|
g |
с |
a |
u |
с |
t |
i |
о |
21 |
s |
s |
g |
0 |
l |
|
i |
n |
e |
q |
u |
a |
1 |
i |
t |
У |
с |
e |
d |
n |