ВУЗ: Не указан
Категория: Не указан
Дисциплина: Не указана
Добавлен: 02.04.2024
Просмотров: 1188
Скачиваний: 3
СОДЕРЖАНИЕ
1. Ознакомьтесь с терминами текста 1.
3. Просмотрите текст 1 еще раз. Ответьте на вопросы, используя информацию текста.
4. Прочтите, переведите и запомните следующие выраже ния:
5. Вспомните образование и случаи употребления The Past Simple Tense.
6. Ознакомьтесь с терминами текста 2
7. Прочтите текст 2 и скажите, что такое компьютер и каковы его основные функции.
9. Найдите в тексте 2 английские эквиваленты следующих словосочетаний:
11. Выполните письменный перевод текста 3 по вариантам.
1. Выберите вариант, который лучше всего выражает глав ную идею текста 2.
2. Вставьте необходимые слова вместо пропусков.
3. Подберите к терминам, данным в левой колонке, определения, представленные справа.
1. Ознакомьтесь с терминами текста 1.
1. Ознакомьтесь с терминами текста 1
2. Прочтите текст и скажите, о каких первых вычислительных приборах рассказывается в нем.
3. Просмотрите текст еще раз. Ответьте на вопросы, используя информацию текста.
5. Переведите следующие цепочки существительных:
6. Подберите к терминам, данным в левой колонке, опре деления, представленные справа.
10. Ответьте на вопросы, используя информацию текста.
11. Найдите в тексте английские эквиваленты следующих словосочетаний:
12. Вспомните значение новых слов и догадайтесь о зна чении их производных.
2. Прочтите текст и скажите, о каких типах компьютеров и сферах их применения вы узнали.
3. Просмотрите текст еще раз. Ответьте на вопросы, ис пользуя информацию текста.
4. Найдите в тексте английские эквиваленты следующих словосочетаний:
5. Образуйте (и переведите) имена существительные от приведенных ниже глаголов с помощью суффиксов:
6. Переведите предложения, содержащие Participle I и Participle II, в функции обстоятельства.
9. Ответьте на вопросы, используя информацию текста.
10. Найдите в тексте английские эквиваленты следующих словосочетаний:
12. Озаглавьте каждый компонент текста и составьте небольшой реферат к нему (по вариантам).
2. Согласуйте слова в левой колонке с их интерпретацией, предложенной справа.
3. Просмотрите текст еще раз. Дайте ответы на вопросы, используя информацию текста.
8. Ознакомьтесь с терминами текста 2.
3. Просмотрите текст еще раз. Ответьте на вопросы, используя информацию текста.
4. Найдите в тексте английские эквиваленты следующих словосочетаний:
6. Найдите в тексте слова, близкие по значению следующим:
7. Переведите предложения, содержащие Perfect Participle Active и Perfect Participle Passive.
8. Ознакомьтесь с терминами текста 2.
14. Выполните письменный перевод текста по вариантам.
4. Найдите в тексте английские эквиваленты следующих словосочетаний:
6. Переведите предложения, содержащие независимый причастный оборот.
14. Ознакомьтесь с терминами текста 3.
3. Ответьте на вопросы, используя информацию текста.
4. Найдите в тексте английские эквиваленты следующих словосочетаний:
12. Расшифруйте следующие аббревиатуры и переведите их.
13. Переведите безличные предложения. Обратите внима ние на их специфику.
14. Вспомните формы причастий, проанализируйте и пе реведите следующие предложения:
16. Прочтите текст и составьте письменно реферат на английском языке.
1. Вставьте необходимые слова вместо пропусков.
2. Прочтите текст и объясните, как вы понимаете термин«компьютерное программирование».
3. Просмотрите текст еще раз и ответьте на вопросы, ис пользуя информацию текста.
4. Найдите в тексте английские эквиваленты следующих словосочетаний:
6. Переведите предложения, содержащие сослагательное наклонение.
8. Прочтите текст и объясните, что представляют собой языки программирования.
13. Выполните перевод следующих текстов письменно по вариантам.
14. Прочтите тексты (по вариантам) и составьте рефераты на английском языке.
3. Определите неличные формы глагола, содержащиеся в следующих предложениях. Переведите их.
3. Просмотрите текст еще раз. Дайте ответы на вопросы, используя информацию текста.
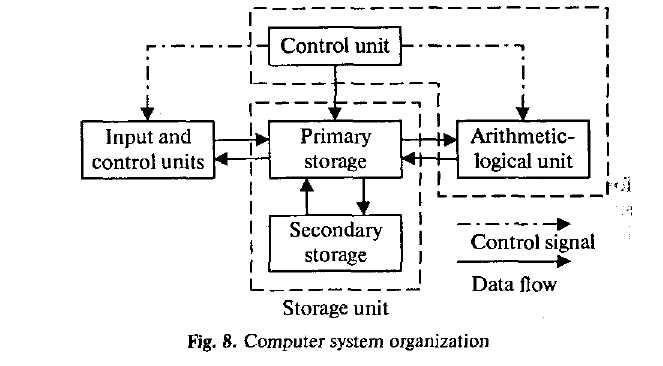
1. What represents the functional organization of a computer? 2. What can we get by studying the functional organization?
3. What is the function of the input device? 4. What does mem ory serve for? 5. What is the task of the arithmetic-logical unit? 6. What is the function of the output? 7. What is the main pur pose of the control unit? 8. How do all units of the computer communicate with each other? 9. What is the additional job of the input? 10. What is the additional function of the output?
4. Найдите в тексте английские эквиваленты следующих словосочетаний:
Функциональная организация; действия компьютера; связывать друг с другом; вводить информацию извне; делать информацию доступной; выполнять вычисления; выводить информацию; блок управления; выдавать команды; заставлять выполнять команды; выходное устройство; внешний мир; связываться друг с другом; комбинация электрических импульсов; холостой импульс; импульсы, распознаваемые компьютером.
75 Unit 6. Functional Organization of the Computer
5 . Разделите
приведенные
ниже слова на три группы, оп
ределяя
по суффиксу часть речи —
существительное,
прилагательное
или наречие. Переведите
слова.
. Разделите
приведенные
ниже слова на три группы, оп
ределяя
по суффиксу часть речи —
существительное,
прилагательное
или наречие. Переведите
слова.
Organization, functional, available, equipment, processor,-Cbmpletely, architectural, converter, convertible, controller, removable, logical, addition, additional, usually, accomplishment, operator, operation, mainly, communication, insertion, electronic, digital, instruction, generally, arithmetic, daily", development, central, lately, visible, substitution, understandable.
6. Вспомните значение новых слов и попытайтесь переве сти словосочетания, употребляемые с этими словами.
Computer, analog computer; digital computer; hybrid computer; all-purpose computer; general-purpose computer; fifth-generation computer; game computer; handheld computer; mobile computer; multimedia computer; notebook computer; pocket computer; portable computer.
Unit: unit of memory; unit of data; unit of measurement; arithmetic unit; arithmetic-logical unit; central processing unit; computing unit; control unit; functional unit; input unit; output unit; network unit; system unit.
Function: arithmetic function; checking function; complex function; computer function; continuous function; conversion function; distribution function; encoding function; logical function; numeric function; output function; program function; search function; software function; support function; utility function; variable function.
Control: access control; batch control; coding control; distance / remote control; error control; execution control; hardware control; input/output control; memory control; power control; production control; program control; rate control; self-acting control; software control; system control.
7. Вспомните значение следующих прилагательных и пре образуйте их в сравнительную и превосходную степени.
A. Small; fast; new; long; late; wide; young; easy; great; dull; rich; bulky; large; vast; early; old; broad.
B. Frequent; reliable; approximate; significant; intricate; possible; basic; remarkable; common; modern; dependent; gen eral; necessary; successful; scientific; universal.
С Good; bad; little; many.
77 Unit
6. Functional
Organization of the Computer
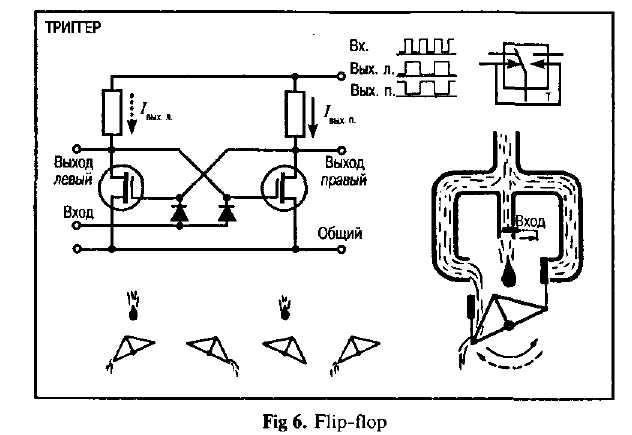
8. Ознакомьтесь с терминами текста 2.
large-scale — большой; крупномасштабный flip-flop — триггер circuit ['ss:kit] — цепь; контур; схема employ [im'ploi] — использовать; употреблять; применять
logic gates — логический элемент; схема пропускания (сигналов); проход
feasible — возможный; выполнимый; осуществимый
interpret orders — интерпретировать, истолковывать команды
operate switches — приводить в действие переключатели
convey [kan'vei] — передавать; сообщать
in response to — в ответ на
correct operand — нужный операнд
original input data — исходная вводимая информация
proceed [pra'si:d] — продолжать(ся); возобновлять(ся); действовать
room — (свободное) место; свободная память
9. Прочтите текст 2 и скажите, какую дополнительную информацию вы узнали о действии основных устройств компьютера.
Text 2. SOME FEATURES OF A DIGITAL COMPUTER
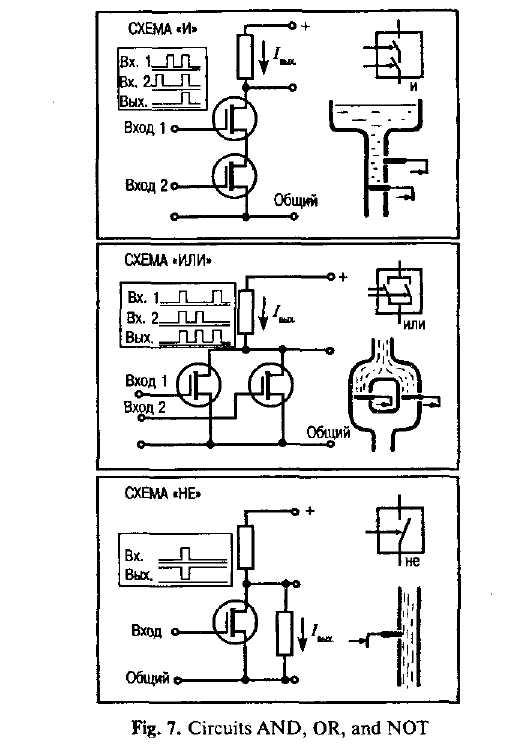
It should be noticed that even in a large-scale digital system, such as in a computer, or in a data-processing, control or digital-communication system, there are only a few basic operations which must be performed. These operations may be operated many times. The four circuits most commonly employed in such systems are known as the OR, AND, NOT and FLIP-FLOP. They are called logic gates or circuits.
An electronic digital computer is a system which processes and stores very large amount of data and which solves scientific
problems of numerical computations of such complexity and with such speed that solution by human calculation is not feasible. So the computer as a system can perform numerical computations and follow instructions with extreme speed but it cannot program itself.
\\fe know that the numbers and the instructions which form the program, the computer is to follow, are stored in an essential part of the computer called the memory. The second important unit of the computer is the control whose function is to interpret orders. The control must convert the command into an appropriate set of voltages to operate switches and carry out the instructions conveyed by the order. The third basic element of a computer is the arithmetic device, which contains the circuits performing the arithmetic computations: addition, subtraction, etc. The control and arithmetic components are called the central processor. Finally a computer requires appropriate input-output devices for inserting numbers and orders into the memory and for reading the final result.
Suppose a command to perform an addition or division has been transmitted to the central processor. In response to this order the control must select the correct operands from the memory, transmit them to the arithmetic unit and return to the
Английский язык. Основы компьютерной грамотности 78
memory the result of the computation. The memory serves for storing not only the original input data, but also the partial results which will have to be used again as the computation proceeds.
Lastly, if the computation doesn't stop with the execution of this instruction and the storage of the partial result, the control unit must automatically pass on to the next instruction. The connection of the control unit back to the input permits insertion of more data when there is room in the memory.
79 Unit & Functional Organization of the Computer
10. Просмотрите текст еще раз. Ответьте на вопросы, ис пользуя информацию текста.
1. What are the most commonly used circuits in any computer? 2. How are they called? 3. What kind of a system is a digital computer? 4. Is there anything that a computer cannot do itself? What is it? 5. Where are the instructions and digits stored? 6. What is the function of the control? 7. What does the arithmetic device serve for? 8. What components form the central processor? 9. What other devices in addition to the above-mentioned ones does a computer require? 10. How are computations performed in a computer?
11. Найдите в тексте английские эквиваленты следующих сочетаний:
Крупномасштабная цифровая система; система обработки данных; система цифровой связи; наиболее широко распространенные схемы; логические схемы; решать научные проблемы; выполнять числовые вычисления; интерпретировать команды; приводить в действие переключатели; выполнять команды; нуждаться (требовать) в необходимом устройстве ввода-вывода; введение чисел и команд; считывание конечных результатов; передавать команду в центральный процессор; в ответ на; хранение частичных результатов; позволить введение новых данных; свободное место в памяти.
12. Подберите пары или группы близких по значению слов из предложенных ниже. Переведите слова на русский язык.
\ferbs: relate, employ, insert, perform, remove, operate, show, interpret, select, issue, use, receive, perform, cause, print, make, compute, connect, execute, take away, require, act, convert, carry out, demand, permit, demonstrate, choose, transmit, type, store, get, calculate, proceed, continue, keep, allow.
Nouns: response, unit, component, computation, storage, gate, amount, digit, element, memory, instruction, device, equipment, connection, circuit, order, command, information, relation, quantity, answer, calculation, number, data.
Adjectives: broad, complete, each, appropriate, every, basic, essential, digital, original, full, wide, initial, major, large, numerical, common, necessary, usual, important, general, great.
1 3. Согласуйте
слова в левой колонке с их интерпретаци
ей,
предложенной справа.
3. Согласуйте
слова в левой колонке с их интерпретаци
ей,
предложенной справа.
1. Functional organization a) processes and stores large of a computer amount of data and solves
problems of numerical computations;
2. Input b) circuits used in large-scale
digital systems;
3. Memory c) method of interrelation of the
main units of a computer
4. Control unit d) removing data from the de-
vice to the outside world;
5. Output e) inserting information into
the computer;
6. Arithmetic unit f) a code of combinations of
electric pulses;
7. Machine language g) performs addition, subtrac-
tion, multiplication, etc;
8. Logic gates h) stores original data as well as
partial results;
9. Digital computer i) causes all parts of the com-
puter to act as a team.
14. Расскажите о действии функциональных устройств компьютера, пользуясь приведенной ниже схемой.
Central processing unit
81 Unit 6. Functional Organization of the Computer
1 5.
Составьте аннотации на русском языке
к следующимтекстам
по вариантам, используйте упр. 14 на с.
52.
5.
Составьте аннотации на русском языке
к следующимтекстам
по вариантам, используйте упр. 14 на с.
52.
1. Logical circuit elements
As it is known, any digital calculation — whether it is performed by 'pencil and paper' methods or with the aid of an automatic computer— must first be broken down into a sequence of elementary arithmetical operations, such as addition, or multiplication. Each such arithmetical operation may be converted into a sequence of simple logical operations. It should be noted that a binary digit may take only two values — "zero" and "one". A logical proposition may be either true or false.
A symbolism and a set of rules suitable for manipulating 'yes or no' logical propositions was developed by George Boole, a self-educated genius who became Professor of Mathematics at Cork University in the middle of the 19lh century. The techniques of Boolean algebra are now extensively used by electrical engineers for the design and analysis of switching circuits. Both the arithmetic and control units of a computer consist of sets of switching circuits for directing and manipulating electrical pulse signals.
The process of combining a number of electronic circuits of known logical properties into an integrated system capable of performing special arithmetical or control functions is known as logical design.
2. The definition of mechanical brain
Let's imagine a railroad line with four stations marked input, storage, computer and output. These stations are joined by little gates or switches to the main railroad line. We can imagine that numbers and other information move along this railroad line, loaded (погруженные) in cars. Input and output are stations where numbers or other information go in and come out respectively. Storage is a station where there are many platforms and where information can be stored. The computer is a special station, somewhat like a factory. When two numbers are loaded on platforms 1 and 2 of this station and the command is loaded on platform 3, then another number is produced on platform^
There is a tower, marked control.This tower runs a telegraph line to each of its little watchmen standing by the gates. The
Английский
язык. Основы компьютерной грамотности 82
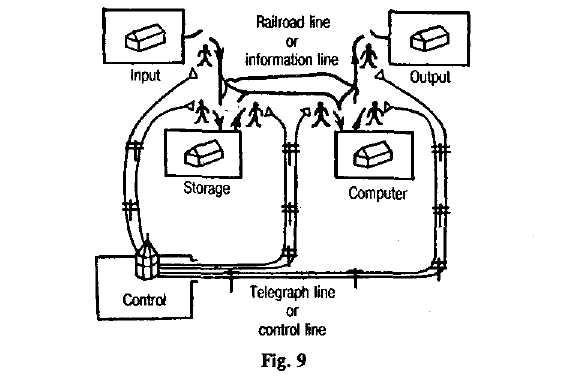
In general, a mechanical brain is made up of: a quantity of registers where information can be stored; channels along which information can be sent; mechanisms that carry out arithmetic and logical operations; a control, which guides the machine to perform a sequence of operations; input and output devices, where information can go into and out of the machine; and at last electricity, which provides energy.
16. Поменяйтесь вариантами и выполните письменный перевод текстов, приведенных выше.
TESTS
1. Подберите вместо пропусков подходящие по смыслу слова.
I. The method of all functional categories to one
another represents the functional organization of a computer, a) showing; b) relating; c) performing
83 Unit 6. Functional Organization of the Computer
2 . Instructions
and data are fed through the equip-
. Instructions
and data are fed through the equip-