ВУЗ: Не указан
Категория: Не указан
Дисциплина: Не указана
Добавлен: 02.04.2024
Просмотров: 1186
Скачиваний: 3
СОДЕРЖАНИЕ
1. Ознакомьтесь с терминами текста 1.
3. Просмотрите текст 1 еще раз. Ответьте на вопросы, используя информацию текста.
4. Прочтите, переведите и запомните следующие выраже ния:
5. Вспомните образование и случаи употребления The Past Simple Tense.
6. Ознакомьтесь с терминами текста 2
7. Прочтите текст 2 и скажите, что такое компьютер и каковы его основные функции.
9. Найдите в тексте 2 английские эквиваленты следующих словосочетаний:
11. Выполните письменный перевод текста 3 по вариантам.
1. Выберите вариант, который лучше всего выражает глав ную идею текста 2.
2. Вставьте необходимые слова вместо пропусков.
3. Подберите к терминам, данным в левой колонке, определения, представленные справа.
1. Ознакомьтесь с терминами текста 1.
1. Ознакомьтесь с терминами текста 1
2. Прочтите текст и скажите, о каких первых вычислительных приборах рассказывается в нем.
3. Просмотрите текст еще раз. Ответьте на вопросы, используя информацию текста.
5. Переведите следующие цепочки существительных:
6. Подберите к терминам, данным в левой колонке, опре деления, представленные справа.
10. Ответьте на вопросы, используя информацию текста.
11. Найдите в тексте английские эквиваленты следующих словосочетаний:
12. Вспомните значение новых слов и догадайтесь о зна чении их производных.
2. Прочтите текст и скажите, о каких типах компьютеров и сферах их применения вы узнали.
3. Просмотрите текст еще раз. Ответьте на вопросы, ис пользуя информацию текста.
4. Найдите в тексте английские эквиваленты следующих словосочетаний:
5. Образуйте (и переведите) имена существительные от приведенных ниже глаголов с помощью суффиксов:
6. Переведите предложения, содержащие Participle I и Participle II, в функции обстоятельства.
9. Ответьте на вопросы, используя информацию текста.
10. Найдите в тексте английские эквиваленты следующих словосочетаний:
12. Озаглавьте каждый компонент текста и составьте небольшой реферат к нему (по вариантам).
2. Согласуйте слова в левой колонке с их интерпретацией, предложенной справа.
3. Просмотрите текст еще раз. Дайте ответы на вопросы, используя информацию текста.
8. Ознакомьтесь с терминами текста 2.
3. Просмотрите текст еще раз. Ответьте на вопросы, используя информацию текста.
4. Найдите в тексте английские эквиваленты следующих словосочетаний:
6. Найдите в тексте слова, близкие по значению следующим:
7. Переведите предложения, содержащие Perfect Participle Active и Perfect Participle Passive.
8. Ознакомьтесь с терминами текста 2.
14. Выполните письменный перевод текста по вариантам.
4. Найдите в тексте английские эквиваленты следующих словосочетаний:
6. Переведите предложения, содержащие независимый причастный оборот.
14. Ознакомьтесь с терминами текста 3.
3. Ответьте на вопросы, используя информацию текста.
4. Найдите в тексте английские эквиваленты следующих словосочетаний:
12. Расшифруйте следующие аббревиатуры и переведите их.
13. Переведите безличные предложения. Обратите внима ние на их специфику.
14. Вспомните формы причастий, проанализируйте и пе реведите следующие предложения:
16. Прочтите текст и составьте письменно реферат на английском языке.
1. Вставьте необходимые слова вместо пропусков.
2. Прочтите текст и объясните, как вы понимаете термин«компьютерное программирование».
3. Просмотрите текст еще раз и ответьте на вопросы, ис пользуя информацию текста.
4. Найдите в тексте английские эквиваленты следующих словосочетаний:
6. Переведите предложения, содержащие сослагательное наклонение.
8. Прочтите текст и объясните, что представляют собой языки программирования.
13. Выполните перевод следующих текстов письменно по вариантам.
14. Прочтите тексты (по вариантам) и составьте рефераты на английском языке.
3. Определите неличные формы глагола, содержащиеся в следующих предложениях. Переведите их.
There is a wide range of secondary storage devices. Typical hardware devices are rotating electromechanical devices. Magnetic tapes, disks, and drums are the secondary storage hardware most often used in computer systems for sequential processing. Magnetic tape, which was invented by the Germans during World War II for sound recording, is the oldest secondary storage medium in common use. Data are recorded in the form of small magnetized "dots" that can be arranged to represent coded patterns of bits.
Tape devices range from large-capacity, high-data-rate units used with large data processing systems to cassettes and cartridges used with small systems. Magnetic disk storage, introduced in the early 1960s, has replaced magnetic tape as the main method of secondary storage. As contrasted with magnetic tapes, magnetic discs can perform both sequential and random processing. They are classified as moving-head, fixed-head, or combination moving-head and fixed-head devices. Magnetic discs are the predominant secondary storage media. They include flexible, or floppy discs, called diskettes. The "floppies" were introduced by IBM in 1972 and are still a popular storage medium to meet the demands of the microcomputer market.
1 0. Ответьте
на вопросы, используя информацию текста.
0. Ответьте
на вопросы, используя информацию текста.
1. How are storage media classified? 2. How is the cost of storage devices expressed? 3. What is the access time for storage media? 4. How does the storage capacity range? 5. What are the two main types of storage devices? 6. What are electronic storage devices? 7. What are the principal primary storage circuit elements? 8. What are the main secondary storage devices? 9. What is the oldest secondary medium and when was it invented? 10. What is a floppy?
11. Найдите в тексте английские эквиваленты следующих словосочетаний:
Запоминающие устройства; носители памяти; первичные ЗУ; вторичные ЗУ; время доступа; стоимость ЗУ; диапазон емкости памяти; архивная память; движущиеся механические части; вращающиеся магнитные ленты и диски; по этим причинам; твердотельные устройства; магнитные сердечники; полупроводники; оперативное ЗУ; аппаратное обеспечение вторичной памяти; звукозапись; . намагниченные точки; представлять зашифрованную комбинацию единиц информации; в отличие от магнитных лент; последовательная и произвольная обработка; устройства с движущейся и фиксированной головкой; удовлетворять потребности; гибкий диск.
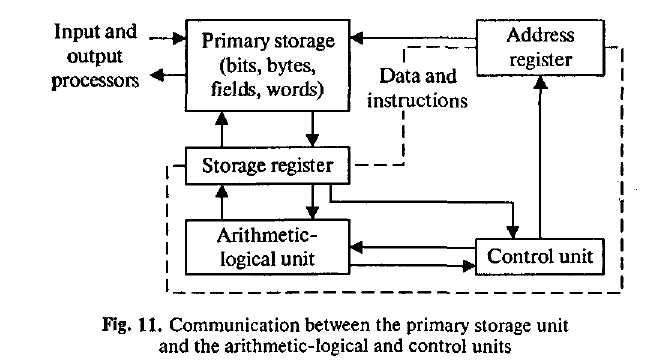
12. Опишите схему.
93 Unit 7. Storage
13. Переведите предложения, содержащие всевозможные формы причастий: Participle I, Participle II, Perfect Participle Active и Perfect Participle Passive.
1. Electromechanical memories depend upon moving mechanical parts for their operation. 2. The time required for the computer to locate and transfer data to and from a storage medium is called the access time. 3. Being not visible software makes possible the effective operation of computer system. 4. Having invented magnetic tapes the Germans used them as the secondary storage medium. 5. When properly programmed computers don't make computational errors. 6. Having been introduced in the early 1960s magnetic disc storage has replaced magnetic tape storage. 7. The control unit interpreting instructions is one of the important parts of any computer system. 8. Data recorded in the form of magnetized dots can be arranged to represent coded patterns of bits. 9. As contrasted with magnetic tapes magnetic discs can perform both sequential and random processing. 10. While having no moving mechanical parts electronic memories can transfer data at very high speed.
14. Выполните письменный перевод текста по вариантам.
DIGITAL COMPUTER OPERATION
1. A digital computer is a machine capable of performing operations on data represented in digital or number form. The individual operations performed by a digital computer are very simple arithmetic or logical processes involving the manipulation of the bits in words or characters of information. The great power of any digital computer rests in the ability to store large volumes of data and to perform these operations at extremely high speed.
In most electronic digital computers the method of number representation is based on the system of binary notation. The binary notation system is most widely used because of the convenience in constructing logical circuits and storage devices capable of handling data in this form. For example, a magnetic memory unit consists of many thousand individual magnetic cells, each of which can be energized in either of two ways to represent the binary digits 0 or 1. If these cells are grouped to form words or binary coded characters, information can be
Английский язык. Основы компьютерной грамотности 94
s tored
for processing in units of specified size. In the same way,digital
data can be recorded as a series of magnetized spots on a magnetic
tape or a magnetic disk.
tored
for processing in units of specified size. In the same way,digital
data can be recorded as a series of magnetized spots on a magnetic
tape or a magnetic disk.
2. The computer has pervaded most fields of human activity and is the most important innovation of our age. Born out of the technology of communication, it is capable of handling enormous amounts of information at tremendous speeds. What makes it so potent is the fact that a single mechanism can perform any information-processing task. The same mechanism can control industrial processes, guide space vehicles or help to teach children. This diversity of tasks is made possible by the simple idea of the stored program.
A program is the enumeration of determining commands. It specifies the method used for the solution of a problem in detail. When the machine is. in operation, both the commands and the numbers to be processed are constantly being taken out of and put into a depository of information known as a memory.
It can be seen that the processes performed by a digital computer are essentially simple. These operations can be performed at extremely high speeds and with a high degree of coordination between the different functional units of the hardware system, and this ability means that digital computers can undertake highly complex tasks.
15. Прочтите внимательно текст. Составьте на английском языке план текста, выделив основные его темы. План можно составить в вопросной, назывной или тезисной форме. Познакомьтесь с образцами планов, представленными после текста; сравните со своим планом.
MEMORY
It is interesting to note that memory, one of the basic components of the computer, is often called storage. It stores calculation program, the calculation formulae, initial data, intermediate and final results. Therefore, the functions of the computer memory may be classified in the following way. Firstly, the computer memory must store the information transmitted from the input and other devices. Secondly, memory should produce the information needed for the computation process to all other devices of the computer.
95 Unit 7. Storage
G enerally,
memory consists of two main parts called themain,
primary or internal, memory and the secondary, or external
memory. The advantage of the primary memory is an extremely
high speed. The secondary memory has a comparatively low speed,
but it is capable of storing far greater amount of
information than the main memory. The primary storage takes
a direct part in the computational process. The secondary
storage provides the information necessary for a single step in
the sequence of computation steps.
enerally,
memory consists of two main parts called themain,
primary or internal, memory and the secondary, or external
memory. The advantage of the primary memory is an extremely
high speed. The secondary memory has a comparatively low speed,
but it is capable of storing far greater amount of
information than the main memory. The primary storage takes
a direct part in the computational process. The secondary
storage provides the information necessary for a single step in
the sequence of computation steps.
The most important performance characteristics of a storage unit are speed, capacity and reliability. Its speed is measured in cycle time. Its capacity is measured by the number of machine words or binary digits. Its reliability is measured by the number of failures (отказ) per unit of time.
План в вопросной форме.
What is memory?
What is the function of memory?
What are the main parts of memory?
What are advantages and disadvantages of a storage unit?
What are their functions?
What are performance characteristics of the main and secondary memory?
What units are performance characteristics measured by?
План в назывной форме
The definition of memory.
The main functions of memoiy.
Classification of memory.
Advantages and disadvantages of memory components.
The functions of memory components.
Performance characteristics of memory.
The units for measuring the performance characteristics of memory.
План в тезисной форме.
Memory is one of the basic components of the comput er.
Memory stores initial data, intermediate and final results.
It produces the information needed to other devices of the computer.
Английский язык. Основы компьютерной грамотности 96
M
 emory
consists of the main (internal) and the secondary
(external) storage.
emory
consists of the main (internal) and the secondary
(external) storage.The main memory has high speed, but small capacity; the secondary memory possesses lower speed but greater ca pacity.
The main memory performs computation; the secondary memory provides information sequentially, step by step.
The performance characteristics — speed, capacity and reliability — are measured by cycles, binary digits and the number of failures per unit of time.
TESTS 1. Вставьте вместо пропусков необходимые слова.
1. The time required for the computer to locate and transfer data in the storage device is called the data time.
a) sequence; b) access; c) value
2. memories have no moving parts.
a) electronic; b) mechanical; c) electromechanical
3. Magnetic were the main elements used for pri mary memory in digital computers for many years.
a) cores; b) tapes; c) disks
4. is more commonly used for memory at present.
a) bipolar semiconductor; b) MOS; c) field-effect transistor
5. Magnetic disks constitute the storage media.
a) internal; b) primary; c)secondary
6. Data are stored in codes in primary as well as in
secondary storage.
a) digital; b) binary; c) numerical
7. Data access time is in electronic memories than
that in electromechanical memories.
a) longer; b) much longer; c) shorter
8. Electronic memories have capacities for data stor-
age.
a) more; b) larger; c) less
97 Unit 7. Storage
2 .
Согласуйте слова левой колонки с их
интерпретацией,предложенной
справа.
.
Согласуйте слова левой колонки с их
интерпретацией,предложенной
справа.
1. Primary a) one of the performance characteris-
tics of storage measured in binary digits;
2. Secondary b) memory that has random access to
the information;
Magnetic disc c) combination of units of information;
Binary codes d) the main method of secondary stor-
age performing both sequential and random storage;
5. RAM e) area of memory where protected pro-
grams can be read from but not written on;
6. Bit f) a fixed number of consecutive bits
representing a character;
7. Byte g) the principal flexible second storage
circuit element;
8. ROM h) part of memory having lower speed
but greater capacity;
9. Floppy i) a unit of information or binary digit;
10. Capacity . j) the most expensive part of memory
having the least capacity and the fastest access time.
Unit 8 CENTRAL PROCESSING UNIT
1 Ознакомьтесь с терминами текста 1.
central processing unit (CPU) - центральный процессор
(ЦП)
interchangeably [,mt3'tfemd33bli] - взаимозаменяемым
образом
precisely [pn'saish] — точно
internal memory - внутренняя память; внутреннее ЗУ activity [sk'tiviti] - деятельность; работа; действия операции to issue ['isju:] - посылать (сигнал); выводить, выдавать
(сообщение) response [n'spons] - ответ; отклик; реакция; отвечать;
реагировать
to interprete [m'tspnt] - интерпретировать; истолковывать;
according to [a'bdin ts] - согласно; в соответствии с level - уровень; степень; мера; выравнивать input-output port - порт ввода-вывода control unit (CU) [bn'troul 'ju:nit] - устройство управления arithmetic-logical unit (ALU) - арифметико-логическое
устройство
switch ['switJl - переключатель; коммутатор; переключать; переходить direct [di'rekt] - направлять; адресовать; указывать;
прямой; непосредственный step-by-step operations - пошаговые операции to select [ss'lekt] - выбирать; выделять (на экране) on the other hand - с другой стороны exponentiation [ekspe'nenji'eifn] - возведение в степень
99 Unit 8. Central Processing Unit
c all
for —требовать;
предусматривать
all
for —требовать;
предусматривать
to load ['loud] — загружать; выполнять загрузку
2. Прочтите текст и скажите, какой компонент составляет сердце компьютерной системы и в чем заключается его функция.
Text 1. CENTRAL PROCESSING UNIT
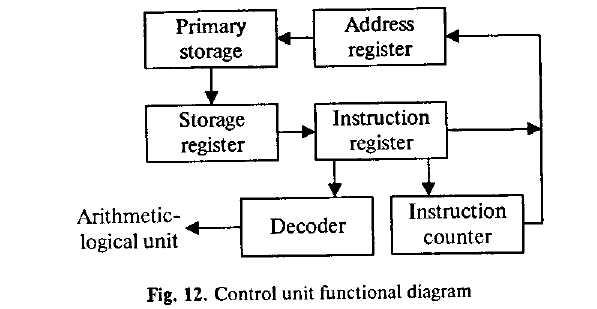
It is well known in computer science that the words 'computer' and 'processor' are used interchangeably. Speaking more precisely, 'computer* refers to the central processing unit (CPU) together with an internal memory. The internal memory, control and processing components make up the heart of the computer system. Manufactures design the CPU to control and carry out basic instructions for their particular computer.
The CPU coordinates all the activities of the various components of the computer. It determines which operations should be carried out and in what order. The CPU controls the operation of the entire system by issueing commands to other parts of the system and by acting on responses. When required it reads information from the memory, interprets instructions, performs operations on the data according to the instructions, writes the results back into the memory and moves information between memory levels or through the input-output ports.
In4igital computers the CPU can be divided into two functional units called the control unit (CU) and the arithmetic-logical unit (ALU). These two units are made up of electronic circuits with millions of switches that can be in one of two states, either on or off.
The function of the CU within the central processor is to transmit coordinating control signals and commands. The control unit is that part of the computer that directs the sequence of step-by-step operations of the system, selects instructions and data from memory, interprets the program instructions, and controls the flow between main storage and the arithmetic-logical unit.
The ALU, on the other hand, is that part of the computer in which the actual arithmetic operations, namely, addition, subtraction* multiplication, division and exponentiation, called for in the instructions are performed.
Английский язык. Основы компьютерной
грамотности 100
3. Просмотрите текст еще раз. Ответьте на вопросы, ис пользуя информацию текста.
1. What words in computer science are used interchangeably and why? 2. What components make up the heart of the computer system. 3. What is the function of the CPU? 4. In what way does the CPU control the operation of the whole system? 5. Name the sequence of operations the CPU performs (use five verbs). 6. What are the CPU functional units made of? 7. What is the function of the CU? 8. What operations are performed in the ALU? 9. Where are data processed? 10. Where are data to be processed loaded into?